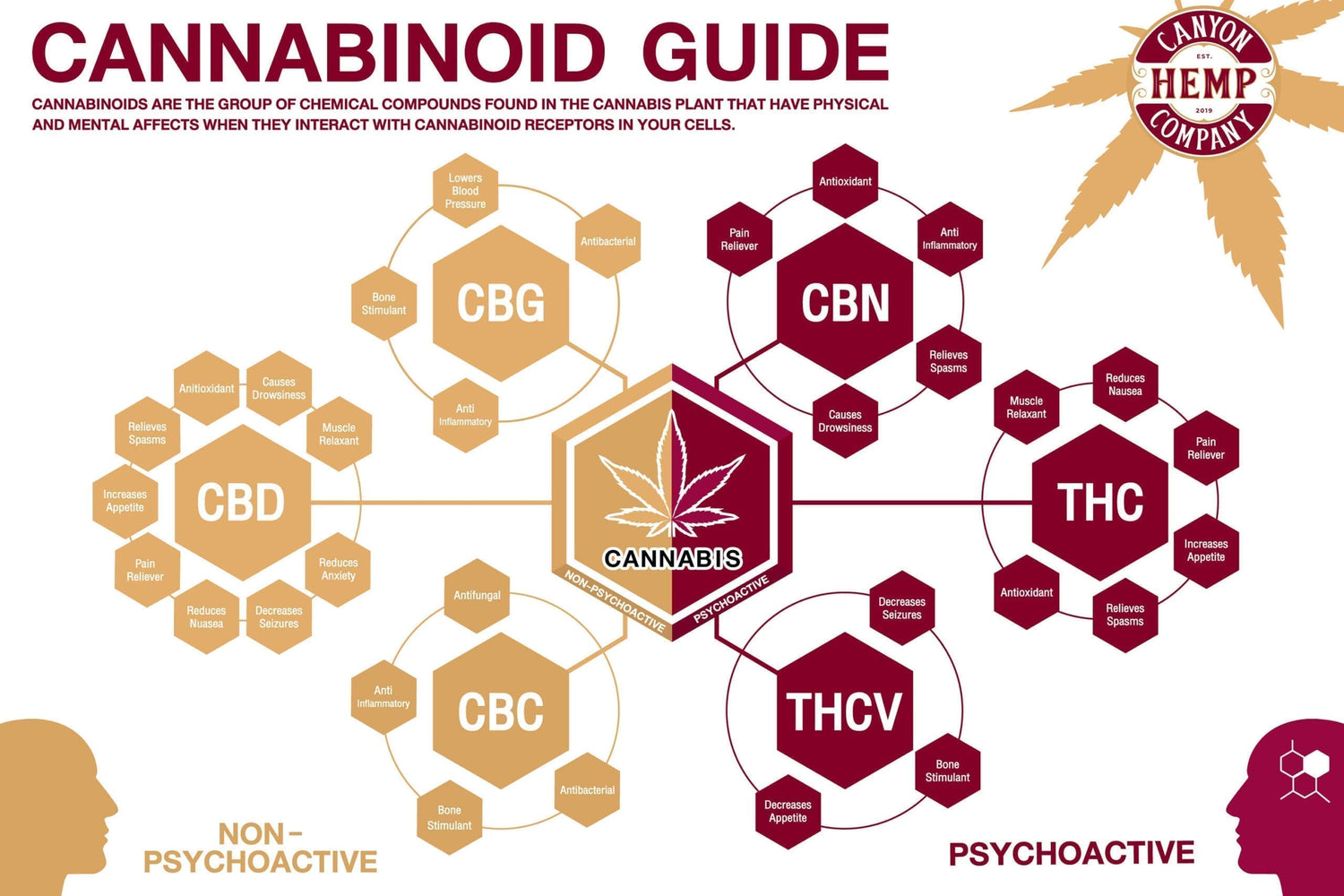
Hemp & CBD
A Guide On CBD & Hemp
Cannabidiol or CBD is part of the Cannabis sativa plant. This plant has been prohibitive for possession in its entirety for decades. Now CBD, one of the many active compounds that is part of the Cannabis sativa plants, is legalized for research and retail purposes. The potential of medical and naturopathic solutions that CBD could cover is astounding. Yet users are able to avoid the psychoactive properties of cannabis containing THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, another compound in the plant.
The Cannabis sativa plant is considered beneficial for fueling the Endocannabinoid System. Here the endogenous receptors pick up the cannabinoids that are found in the cannabis plant.
Depending on your condition, you can choose a variety of treatment methods for using CBD. This includes creams that are absorbed in the skin, as well as edibles and oral ingestion methods via tinctures. You can also smoke CBD in its dried flower form or vape CBD oil.

How CBD Works
The use of cannabis in the body functions by attaching to receptors in the Endocannabinoid System (ECS). This is where the brain picks up the various cannabinoids from the cannabis plant when it is consumed. If you are consuming CBD or THC, the CB1 receptor is activated.
Studies have found that when you use cannabinoids, your body uses them in the most natural and beneficial ways. When we are out of balance, chemically. Our body will naturally try to self-regulate. The body achieves homeostasis using the ECS and our own natural cannabinoids called Endocannabinoids. Cannabinoids from the Sativa L plant (Phytocannabinoids) act as endocannabinoids when ingested. The results are a healthy ECS that makes it easier for the brain to achieve homeostasis
